SharePoint 2013 CRUD Operation to List Using Rest API
CRUD Operation to List Using SharePoint 2013 Rest API
This post will give you a complete idea about CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operation in a list of SharePoint 2013 using REST API.
REST service for list was first introduced in SharePoint 2010. It was under the end point /_vti_bin/listdata.svc, and it still works in SharePoint 2013. SharePoint 2013 introduces another endpoint /_api/web/lists, and which is much more powerful than in SharePoint 2010. The main advantage of REST in SharePoint 2013 is: we can access data by using any technology that supports REST web request and Open Data Protocol (OData) syntax. That means you can do everything just making HTTP requests to the dedicated endpoints. Available HTTP methods are GET, POST, PUT, MERGE, and PATCH.
READ: HTTP GET method is used for any kinds of read operation.
CREATE: Any kind of create operation like list, list item, site and so on maps to the HTTP POST method. You have to specify the data in request body and that’s all. For non‐required columns, if you do not specify the values, then they will be set to their default values. Another important thing is: you cannot set value to the read‐ only fields. If you do so, then you will get an exception.
UPDATE: For updating existing SharePoint 2013 objects, there are three HTTP methods like PUT, PATCH and MERGE available. The recommended methods are PATCH and MERGE. PUT requires the entire huge object to perform update operation. For example we have a list named PRODUCTS and it has 100+ fields and we want to update ProductName field only. In this case, if we use PUT method, we must have to specify the value of others fields along with ProductName field. But PATCH and MERGE are very easy. We just have to specify the value of ProductName filed only.
DELETE: HTTP DELETE method is used to delete any objects in SharePoint 2013.
The result will be in data.d.results, In that you will find fields internal names as object’s property.
In the above example, we will get only the Id of Lookup and Person type column. But we need more information about these columns in our JSON results. To get the exact value, we have to learn some query string operators.
$select specifies which fields to return in JSON results.
$expand helps to retrieve information from Lookup columns.
Now if we re‐write the urlToGetAllItems, it should look like the following:
To use $expand along with $select, you have to specify the column names in $select just what I did in the above like MyLookup/Title, MyLookup/ID.
$filter specifies which items to return. If I want to get the items where Title of MyTutorial equals to‘Sample tutorial’ and ID of MyTutorialParent equals to 1, the URL should look like the following:
In the above example query, you may notice that there are query operator like ‘eq’ in above URL. Now let’s see what are the other query operators available.
We can use the following method for updating an item.
This post will give you a complete idea about CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operation in a list of SharePoint 2013 using REST API.
REST service for list was first introduced in SharePoint 2010. It was under the end point /_vti_bin/listdata.svc, and it still works in SharePoint 2013. SharePoint 2013 introduces another endpoint /_api/web/lists, and which is much more powerful than in SharePoint 2010. The main advantage of REST in SharePoint 2013 is: we can access data by using any technology that supports REST web request and Open Data Protocol (OData) syntax. That means you can do everything just making HTTP requests to the dedicated endpoints. Available HTTP methods are GET, POST, PUT, MERGE, and PATCH.
READ: HTTP GET method is used for any kinds of read operation.
CREATE: Any kind of create operation like list, list item, site and so on maps to the HTTP POST method. You have to specify the data in request body and that’s all. For non‐required columns, if you do not specify the values, then they will be set to their default values. Another important thing is: you cannot set value to the read‐ only fields. If you do so, then you will get an exception.
UPDATE: For updating existing SharePoint 2013 objects, there are three HTTP methods like PUT, PATCH and MERGE available. The recommended methods are PATCH and MERGE. PUT requires the entire huge object to perform update operation. For example we have a list named PRODUCTS and it has 100+ fields and we want to update ProductName field only. In this case, if we use PUT method, we must have to specify the value of others fields along with ProductName field. But PATCH and MERGE are very easy. We just have to specify the value of ProductName filed only.
DELETE: HTTP DELETE method is used to delete any objects in SharePoint 2013.
For accessing SharePoint resources by using REST API, at first we have to find the appropriate endpoints. The following table demonstrates the endpoints associated
with CRUD operation in a list
Accessing REST endpoints
from client side, there are so many ways but the approach is almost same everywhere. All examples are given using jQuery.ajax, but you can use any REST Client like Fiddler, Postman or Advanced REST Client and so on.
URL endpoint
|
Supported HTTP Method
|
Description
|
/_api/Web/Lists
|
GET, POST
|
Retrieving all lists in a site and adding new lists
|
/_api/Web/Lists/GetByTitle('list name')
|
GET, POST
|
Getting a list details by its title and updating it as well. If anyone
changes your list title, your code will break.
|
/_api/Web/Lists(guid'guid id of your list')
|
GET, POST
|
Same as above but changing list title will not affect the code.
|
/_api/Web/Lists/GetByTitle(' listname ')/Fields
|
GET, POST
|
Retrieving all fields associated with a list and add new fields
|
/_api/Web/Lists/GetByTitle('list name')/
Fields/GetByTitle('fieldname')
|
GET, PUT, PATCH, MERGE, DELETE
|
Getting details of a field, modifying and deleting it.
|
/_api/Web/Lists/GetByTitle('list name') /Items
|
GET, POST
|
Retrieving all items in a list and adding new items
|
/_api/web/lists/GetByTitle('list name') /GetItemById(itemId)
|
GET, PUT, PATCH, MERGE, DELETE
|
This endpoint can be used to get, update and delete a single item.
|
GET Items From List
At first, create our method to get items from a particular list. If we use $.ajax, it should look like the following:
In the above code, _spPageContextInfo.webAbsoluteUrl will returns the current site url and it’s the preferred way rather typing
it hard coded. Now we will get some urls to call the above method.
Getting All Items from List
If we go through the REST endpoints table again, the endpoint (constructed url) should look like the following:
Call the method SampleGetItems(urlToGetAllItems);
Call the method SampleGetItems(urlToGetAllItems);
The result will be in data.d.results, In that you will find fields internal names as object’s property.
In the above example, we will get only the Id of Lookup and Person type column. But we need more information about these columns in our JSON results. To get the exact value, we have to learn some query string operators.
$select specifies which fields to return in JSON results.
$expand helps to retrieve information from Lookup columns.
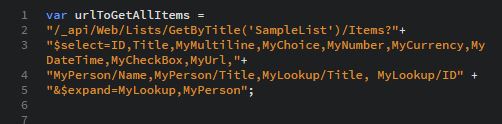
Now if we re‐write the urlToGetAllItems, it should look like the following:
To use $expand along with $select, you have to specify the column names in $select just what I did in the above like MyLookup/Title, MyLookup/ID.
$filter specifies which items to return. If I want to get the items where Title of MyTutorial equals to‘Sample tutorial’ and ID of MyTutorialParent equals to 1, the URL should look like the following:
In the above example query, you may notice that there are query operator like ‘eq’ in above URL. Now let’s see what are the other query operators available.
Numeric
|
String
|
Date Time functions
|
Lt (less
than)
|
startsWith (if starts with some string value)
|
day()
|
Le (less
than or equal)
|
substringof (if contains any sub string)
|
month()
|
Gt (greater
than)
|
year()
|
|
Ge (greater
than or equal)
|
hour()
|
|
Eq (equal
to)
|
Eq
|
minute()
|
Ne (not
equal to)
|
Ne
|
second()
|
$orderby is used to sort items. Multiples fields are allowed separate by comma. Ascending or descending order can be specified just by appending the asc or desc
keyword to query.
$top is used to apply paging in items.
Adding New Item
In this case, our HTTP method will be POST. So write a method for it.
URL and request body will be like the following for adding new item in list
Note: Properties of data are the internal names of the fields. We can get it from following URL by making a HTTP GET request.
In header, you have to specify the value of X‐RequestDigest. It’s a hidden field inside the page, you can get its value by the above mentioned way ($("#__REQUESTDIGEST").val()). But sometimes, it does not work. So the appropriate approach is to get it from /_api/contextinfo. For this, you have to send a
HTTP POST request to this URL (_api/contextinfo) and it will return X‐RequestDigest value (in the JSON result, its name should be
FormDigestValue).
URL and request body will be like the following for adding new item in list.
How to specify the value of __metadata for new list item? Actually, it looks like the following.
Or we can get it it from following URL by sending a GET request.
Updating Item
There are quite difference in update item when compared to add new item. Lets look one by one.
- Now HTTP method is PATCH and it is also specified in header ("X‐Http‐ Method": "PATCH") and which is recommended I mentioned earlier.
- etag means Entity Tag which is always returned during HTTP GET items. You have to specify etag value while making any update or delete request so that SharePoint can identify if the item has changed since it was requested. Following are the ways to specify etag.
1. "If‐Match": oldItem.__metadata.etag (If etag value does not match, service will return an exception)
2. "If‐Match": "*" (It is considered when force update or delete is needed)
We can use the following method for updating an item.
Then you can get your old item, modify it and construct the URL.
Deleting Item
It’s very simple. Just the following method can do everything.
URL is the same as updating item. It will not return anything when operation is successful. But if any error happens, then it will return an exception.















Comments
Post a Comment